Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
In veterinary practice, especially in ruminant health management, recognizing the visual signs of abdominal distension is crucial. Two common conditions that present with abdominal bloating in cattle are Tympany (bloat) and Vagal Indigestion
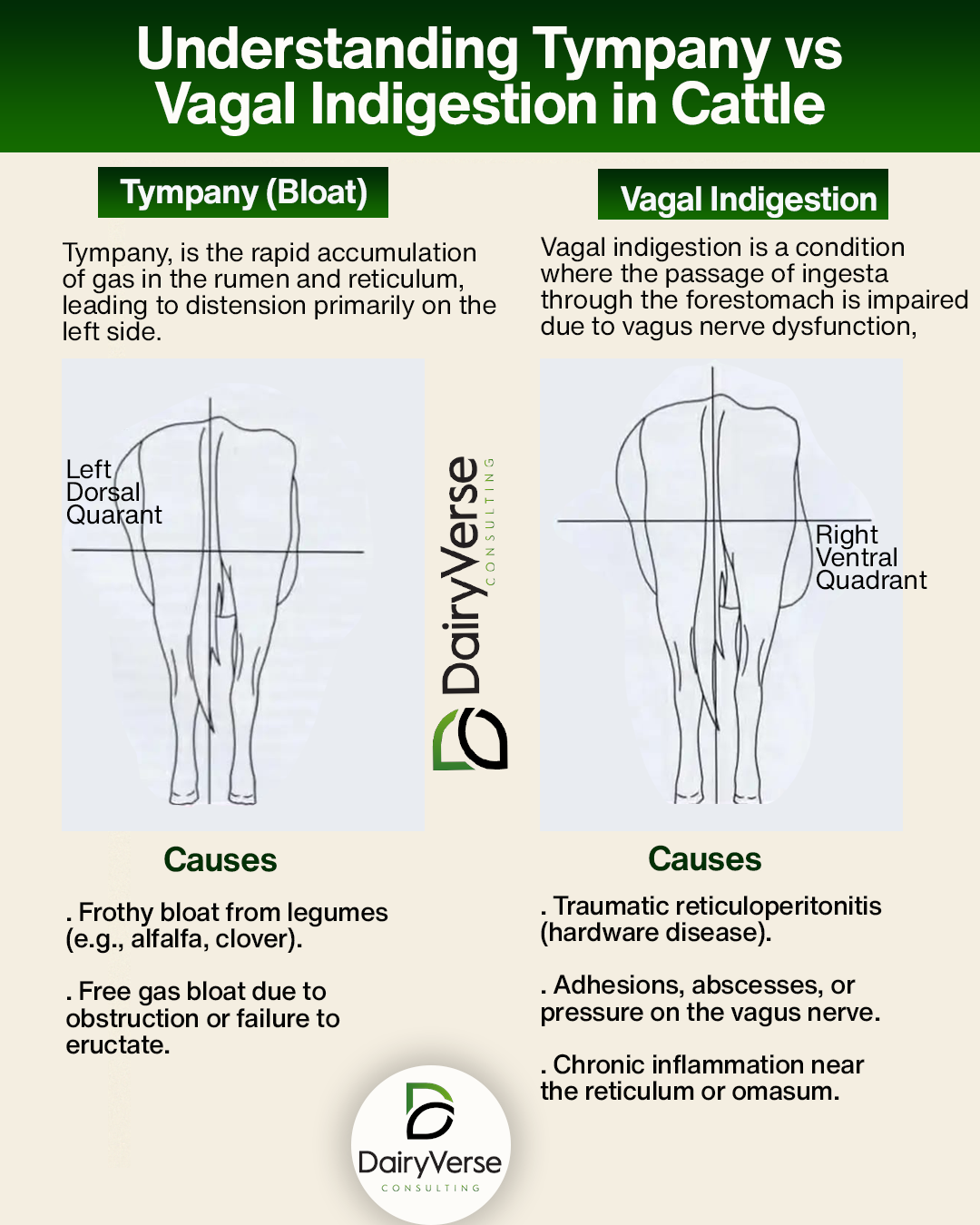
In veterinary practice, especially in ruminant health management, recognizing the visual signs of abdominal distension is crucial. Two common conditions that present with abdominal bloating in cattle are Tympany (bloat) and Vagal Indigestion. Though they may appear similar, their causes, presentation, and treatment differ significantly.
Definition:
Tympany, commonly known as bloat, is the rapid accumulation of gas in the rumen and reticulum, leading to distension primarily on the left side.
Visual Appearance:
Causes:
Clinical Signs:
Treatment:
Definition:
Vagal indigestion is a condition where the passage of ingesta through the forestomach is impaired due to vagus nerve dysfunction, often leading to chronic distension of the rumen and other compartments.
Visual Appearance:
Causes:
Clinical Signs:
Treatment:
| Condition | Left Dorsal | Right Ventral | Appearance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tympany | Distended | Normal | Left-side balloon |
| Vagal Indigestion | Distended | Distended | “Papple” shape |
Proper identification of the quadrant involved in abdominal distension helps in quickly narrowing down the possible cause and initiating the correct treatment. Tympany is an emergency, often requiring rapid gas release, while vagal indigestion is more chronic and requires a detailed approach to diagnosis and management.