How to Raise a Bull for Meat Production
Raising a bull for meat requires careful selection, proper feeding, health management, and humane handling to ensure optimal growth, meat quality, and profitability.
No products in the cart.
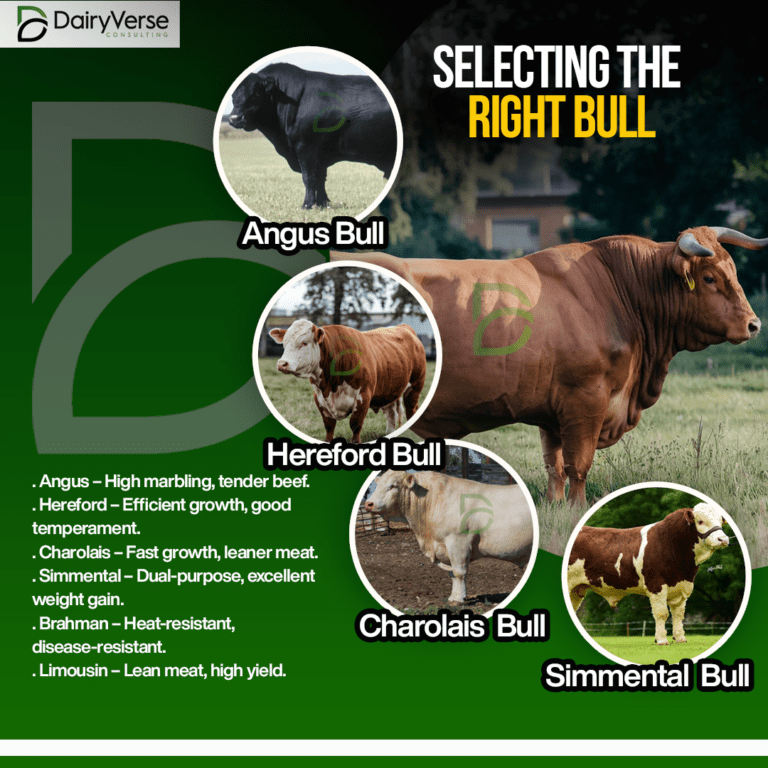
Raising a bull for meat requires careful selection, proper feeding, health management, and humane handling to ensure optimal growth, meat quality, and profitability.

Silage is an essential feed source for livestock, offering a cost-effective and nutritious alternative during periods of feed scarcity.

Silage is an essential component in the diet of livestock, especially during the lean seasons when fresh forage is scarce.

In dairy farming, maintaining the health and productivity of cows is essential for both economic and animal welfare reasons. Among the many factors that influence a cow’s well-being, trace elements play a critical role in ensuring optimal growth, reproduction, and milk production. A deficiency in trace elements can lead to noticeable symptoms, including changes in coat color, reduced fertility, and compromised milk yield.

Silent heat, also known as subestrus, is a condition in which a heifer or cow undergoes normal ovarian cycles and ovulates but fails to display the noticeable signs of estrus (heat) that are typically associated with breeding readiness.

Ticks are a significant threat to the health and productivity of dairy cows. These parasites not only cause discomfort but also severely impact milk production and overall profitability.
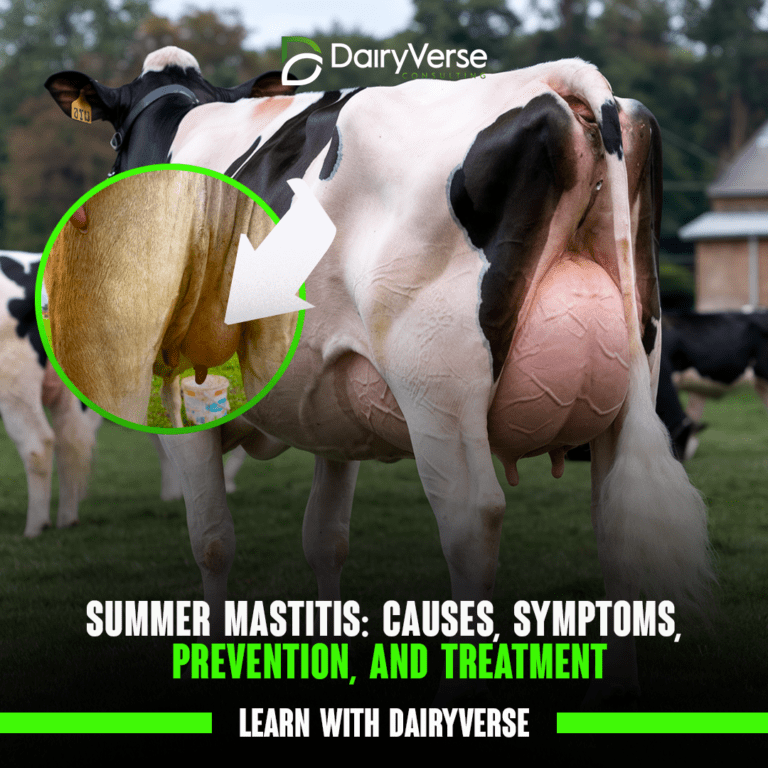
Summer mastitis is a seasonal and costly condition affecting dairy and beef cows, particularly during the warm months.
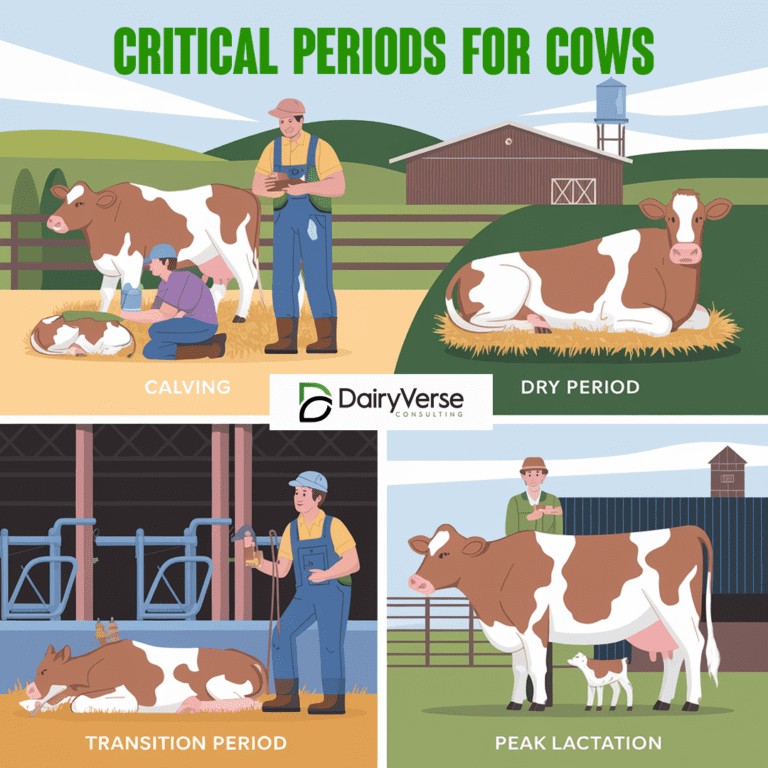
Cows experience several critical periods that require focused care and management to maintain their health and productivity. Proper planning during these stages minimizes risks and maximizes output.

Black Quarter (BQ), also known as Blackleg, is one of the most devastating diseases that can affect cattle. Caused by the bacterium Clostridium chauvoei, this disease is often fatal and requires immediate attention. Understanding its causes, symptoms, prevention, and treatment is essential for cattle farmers to protect their herds.