How to Raise a Bull for Meat Production
Raising a bull for meat requires careful selection, proper feeding, health management, and humane handling to ensure optimal growth, meat quality, and profitability.
No products in the cart.
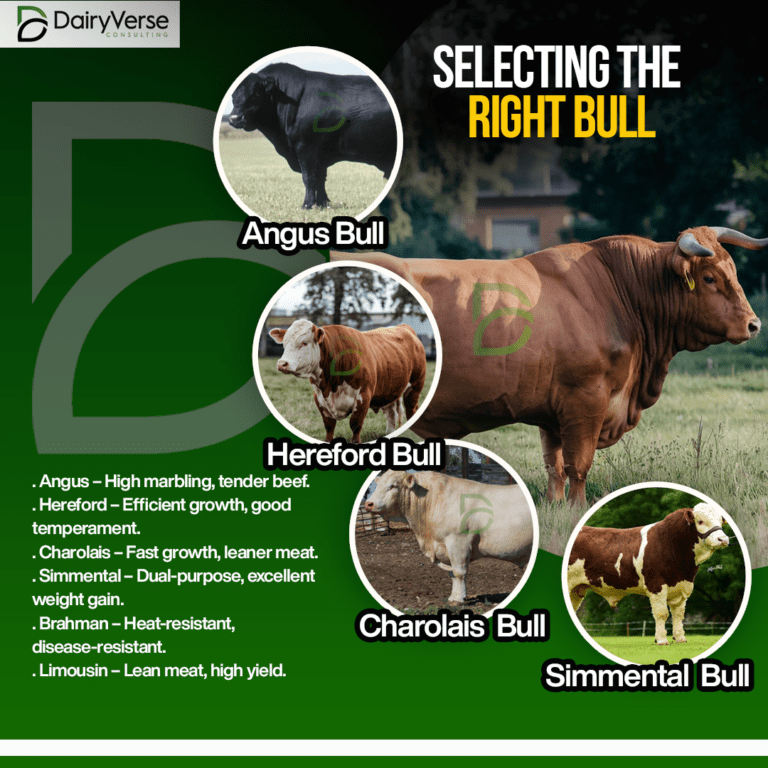
Raising a bull for meat requires careful selection, proper feeding, health management, and humane handling to ensure optimal growth, meat quality, and profitability.

Ticks are a significant threat to the health and productivity of dairy cows. These parasites not only cause discomfort but also severely impact milk production and overall profitability.
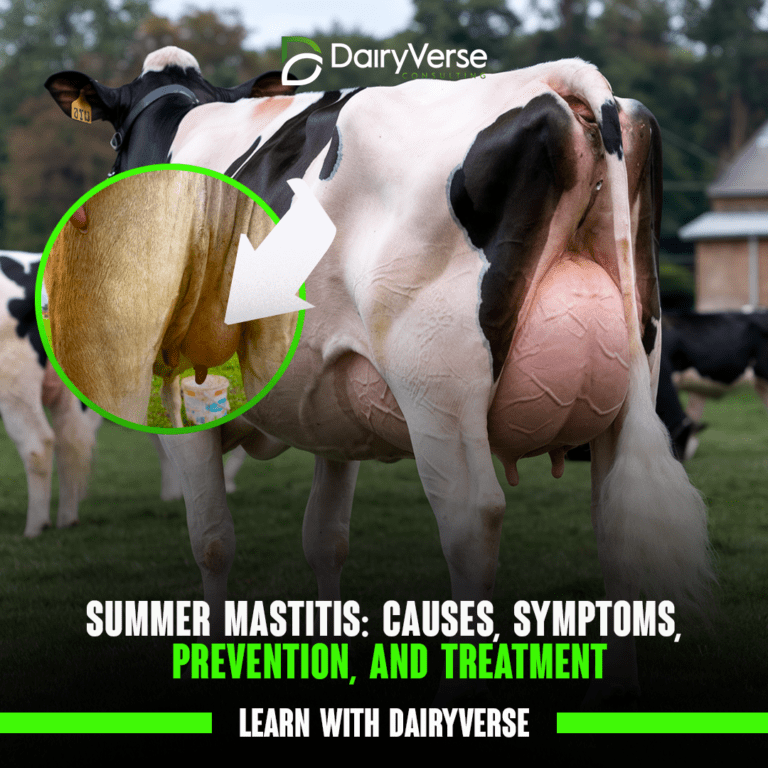
Summer mastitis is a seasonal and costly condition affecting dairy and beef cows, particularly during the warm months.
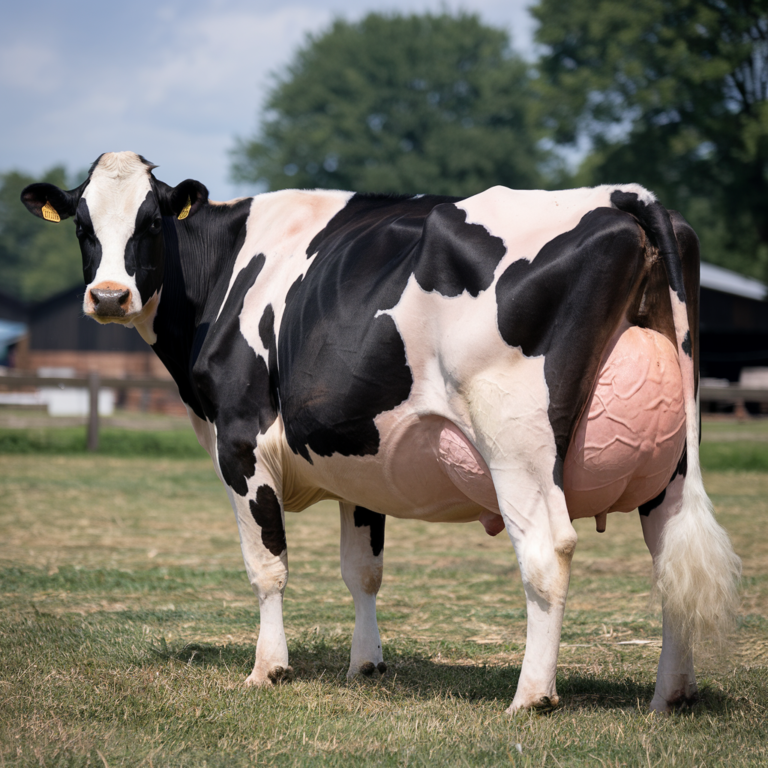

For dairy farmers aiming for optimal milk production, managing the days in milk (DIM) is crucial. DIM refers to the period after calving during which a cow produces milk. The target for an all-year-round calving herd is to maintain an average of 180 days in milk

Anaplasmosis is a significant infectious disease in cattle, impacting herds across tropical and subtropical regions. This condition, caused by the bacterium Anaplasma marginale, can lead to severe anemia, reduced productivity, and economic losses if not managed promptly.