Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
While both types of beef provide protein and essential nutrients, they differ significantly in how the cattle are raised, their nutritional profiles, and their overall effects on human health.
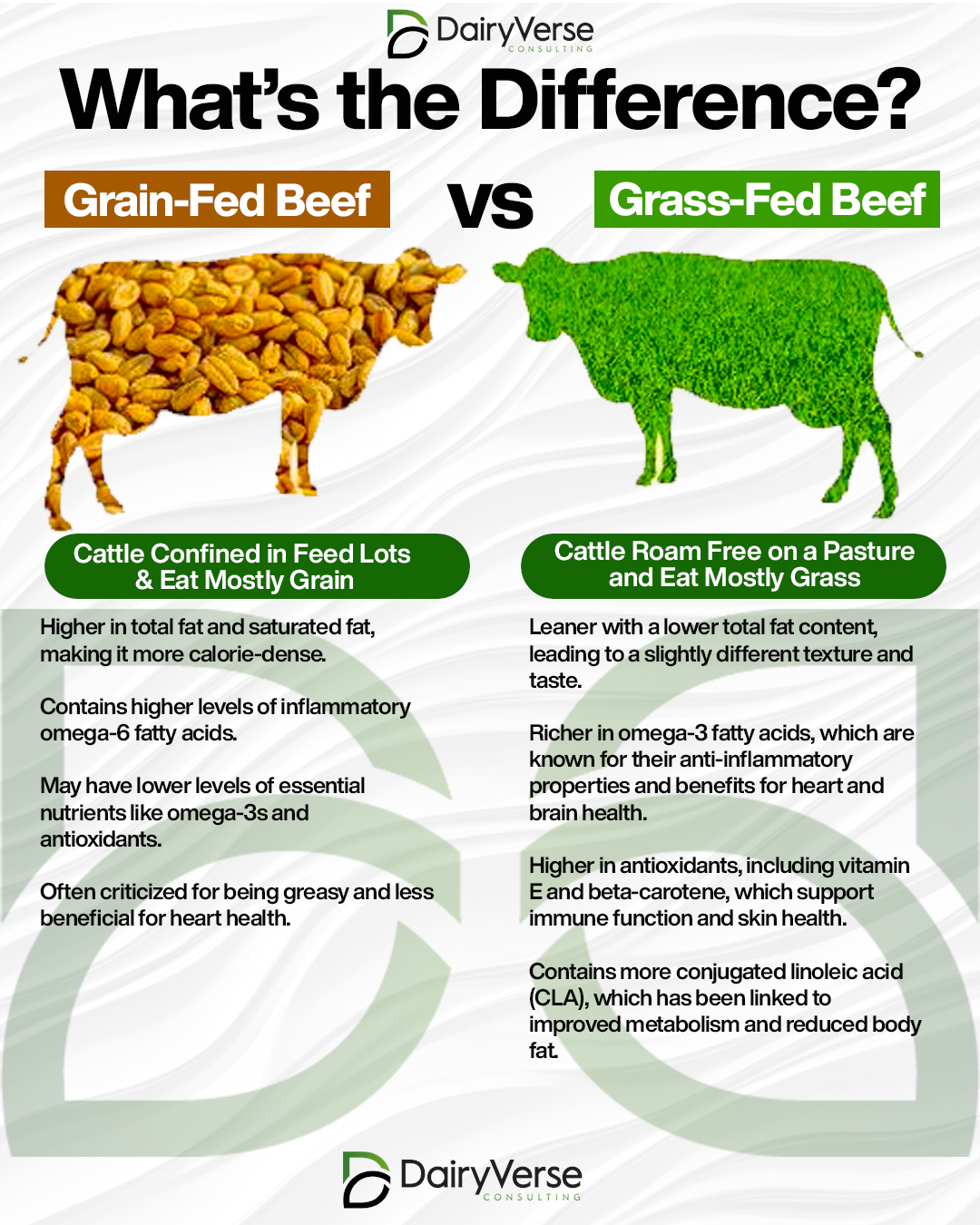
In recent years, the debate between grass-fed and grain-fed beef has gained momentum as consumers become more conscious of their dietary choices and their impact on health and the environment. While both types of beef provide protein and essential nutrients, they differ significantly in how the cattle are raised, their nutritional profiles, and their overall effects on human health. Understanding these differences can help consumers make informed choices.
Grain-Fed Beef:
Grass-Fed Beef:
The differences in diet lead to distinct nutritional profiles between grass-fed and grain-fed beef. Here’s how they compare:
Grain-Fed Beef:
Grass-Fed Beef:
Due to its higher omega-3 and antioxidant content, grass-fed beef is often considered the healthier option. Some of the benefits include:
However, grain-fed beef is often more accessible and affordable, making it the preferred choice for many consumers. While it may have a higher fat content, moderation and a balanced diet can help mitigate potential health risks.
Grass-fed beef is often associated with more sustainable and humane farming practices. Since these cattle graze on natural pastures, they contribute to soil health and biodiversity. Conversely, grain-fed cattle raised in feedlots require significant amounts of grain, water, and land, leading to higher environmental impacts such as deforestation, soil degradation, and increased greenhouse gas emissions.
From an ethical standpoint, grass-fed cattle typically have better living conditions compared to those in confined feedlots. The freedom to graze and a more natural diet align with humane farming practices.
The decision between grass-fed and grain-fed beef depends on personal preferences, health goals, and budget considerations. Here are some key takeaways:
Regardless of the choice, it is essential to consume beef as part of a balanced diet that includes a variety of nutrient-dense foods. Opting for quality sources and considering the impact of your dietary choices can lead to better health and a more sustainable food system.
The grass-fed vs. grain-fed beef debate highlights the importance of understanding where food comes from and how it impacts health and the environment. While both options have their advantages, grass-fed beef stands out as a healthier and more sustainable choice. However, personal preferences and budget constraints also play a crucial role in making the best decision for you and your family. As awareness grows, more consumers are seeking transparent labeling and ethical sourcing, making it easier to choose high-quality beef that aligns with their values.