Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Address
304 North Cardinal
St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124
Work Hours
Monday to Friday: 7AM - 7PM
Weekend: 10AM - 5PM
Two prevalent diseases affecting livestock today are Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) and Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD). In this article, we will break down their causes, signs, and the control measures you can adopt to protect your herd.
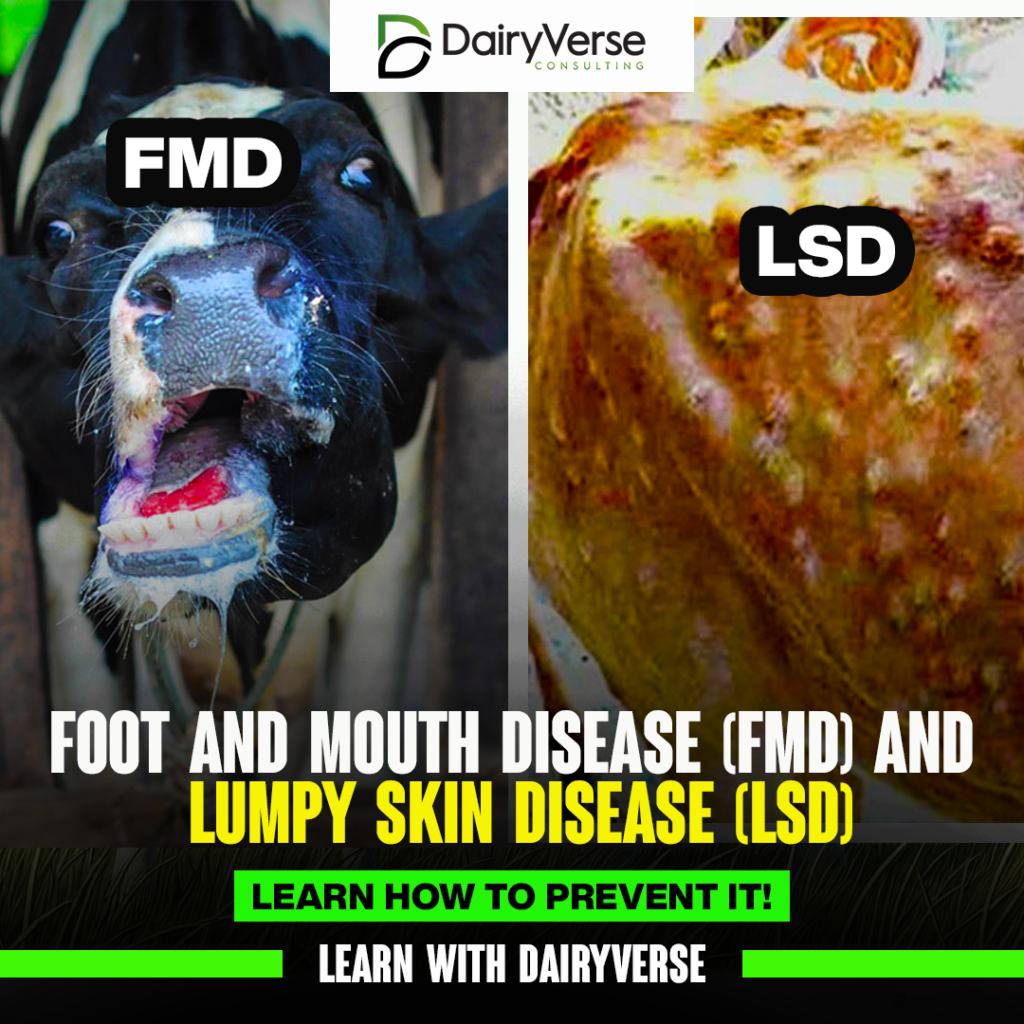
Livestock diseases are a major concern for farmers worldwide, as they can lead to significant economic losses and reduced productivity. Two prevalent diseases affecting livestock today are Foot and Mouth Disease (FMD) and Lumpy Skin Disease (LSD). In this article, we will break down their causes, signs, and the control measures you can adopt to protect your herd.
FMD is a highly contagious viral disease that primarily affects animals with divided hooves, such as cattle, sheep, goats, and pigs. The disease spreads rapidly through the air, making early detection and preventive measures critical.
Key Signs and Symptoms:
Treatment and Control:
Antibiotic Cover: Used to prevent secondary infections.
Vaccination: Farmers are advised to vaccinate livestock with Fotivax multivariant every three months.
Recovery Boost: Administer Booster+® to previously infected animals to enhance their recovery rate.
Early intervention and routine vaccination are crucial in managing FMD outbreaks. Farmers should isolate infected animals and sanitize affected areas to limit the spread.
LSD is another viral disease that mainly affects cattle and, to a lesser extent, sheep and goats. Unlike FMD, LSD is transmitted through biting insects, such as tsetse flies and mosquitoes, making insect control a key aspect of prevention.
Key Signs and Symptoms:
Treatment and Control:
Antibiotic Cover: Helps to prevent bacterial complications.
Vaccination: Use Lumpivax Neethling strain once a year to protect livestock.
Managing the insect population around farms through insecticide sprays, proper drainage, and clean environments can significantly reduce LSD transmission.
Best Practices for Farmers
Vaccination Schedule: Regular vaccinations as recommended above are vital for disease prevention.
Early Detection: Monitor livestock daily for any signs of illness.
Hygiene and Biosecurity: Maintain clean shelters and implement biosecurity measures to prevent the entry and spread of pathogens.
Isolate Infected Animals: Separate symptomatic animals immediately to protect the rest of the herd.
Educate Farm Workers: Ensure all workers understand the signs and know how to act in case of outbreaks.
Final Thoughts
Diseases like Foot and Mouth Disease and Lumpy Skin Disease highlight the importance of preventive measures in livestock farming. By staying informed and proactive, farmers can minimize losses and ensure healthier herds. Regular veterinary consultations and adherence to vaccination schedules can go a long way in safeguarding livestock and sustaining productivity